Bladder Pain Syndrome (BPS)
Interstitial cystitis (IC) or bladder pain syndrome is a chronic, benign condition of the bladder. The bladder lining is severely inflamed. In many cases, this inflammation is not caused by bacteria as in a normal bladder infection. In most cases, antibiotics do not help.
Cause
- The cause of BPS is not fully known, we know that there are multiple causes, such as:
- an allergy, a surgery
- an inflammation
- a virus
- a disorder in the immune system
- In addition, factors from our environment can play a role, such as our diet. BPS is not caused by stress, but it can worsen the symptoms.
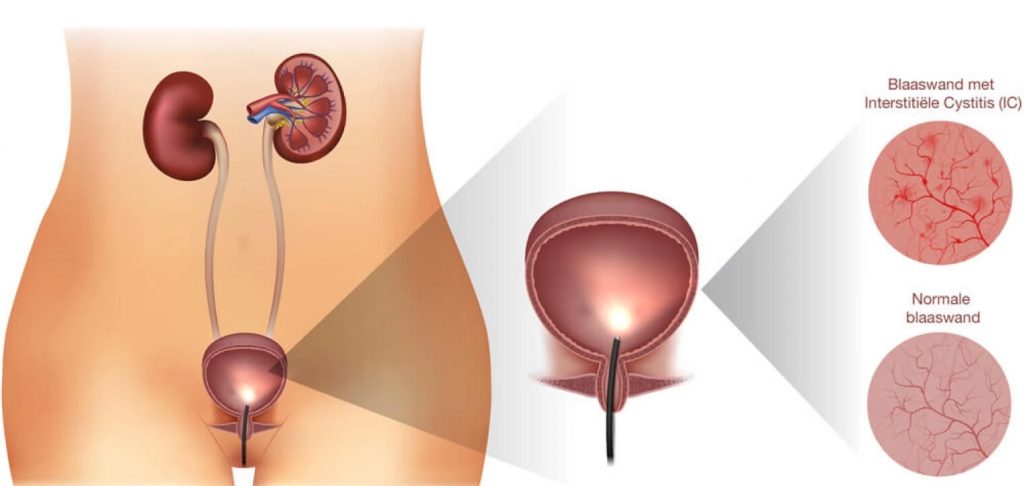
Symptoms that often occur with bladder pain syndrome:
- Pain in the lower abdomen, which can sometimes extend to the back, groin, or flanks
- In women: pain in the vagina
- In men: pain in the penis, testicles, and scrotum
- Pain that increases as the bladder gets fuller, urinating relieves the pain and gives a feeling of relief
- In women: before menopause, symptoms often worsen just before menstruation
- Constant urge to urinate
- Frequent urination, including at night
Possible treatments
Unfortunately, this condition cannot be cured, but there are treatments to reduce the symptoms. The most well-known are:
- Medications (prescription)
- Pain medication and anti-inflammatory drugs. Medication will relax the bladder and can reduce urgency
- PTNS–neurostimulation, in PTNS the nerves that lead to the bladder are stimulated by electrical impulses, which often reduces urgency
- Bladder instillation, which inhibits inflammation and/or restores the GAG layer
- Laser treatment, the pain spots and ulcers (Hunner’s lesions) in the bladder can be treated with a laser
- Botox injections in the bladder lining
- Surgery
In some cases, when the bladder is severely damaged, bladder capacity is greatly reduced, and there is a lot of pain, surgery may be necessary. The bladder is then removed. The urologist creates a urostomy or a new bladder can be made from a piece of the intestine.